
The Next and Already 15th Magnetic Carrier Meeting Will Be in Paris, France
March 24, 2025Picture
Magnetic Nanoparticles Transport Drugs Deep Into Tumors With Magnet's Help
March 24, 2025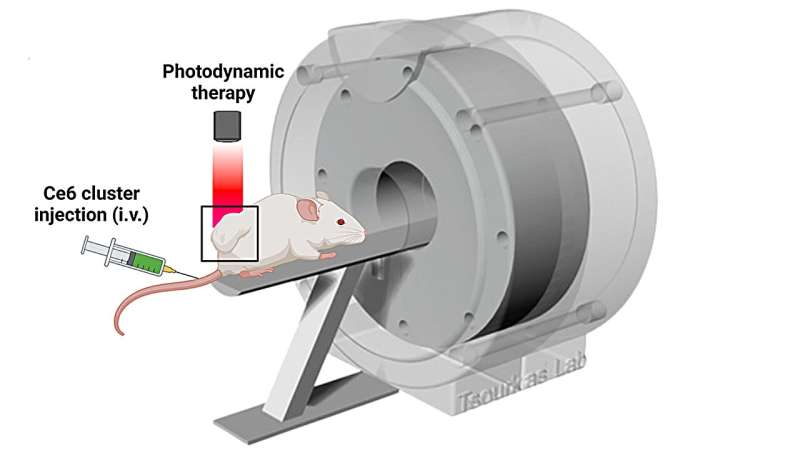 Drugs and other treatments can be quite effective at killing cancer cells, yet many fall short as they struggle to penetrate deep into solid tumors due to physical barriers within the tissue. But in a recent study published in ACS Nano, Andrew Tsourkas, Zhiliang Cheng et al. may have found a way to pull them through.
Drugs and other treatments can be quite effective at killing cancer cells, yet many fall short as they struggle to penetrate deep into solid tumors due to physical barriers within the tissue. But in a recent study published in ACS Nano, Andrew Tsourkas, Zhiliang Cheng et al. may have found a way to pull them through.
This team of bioengineers at the University of Pennsylvania transported therapeutic magnetic nanoparticles into the depths of tumors by tugging at them with an external magnetic device, based on 8 Halbach arrays. Working in a mouse model of triple-negative breast cancer, the researchers used their approach to slow tumor growth far more than treatment with nanoparticles not exposed to a magnetic field. In addition, the nanoparticles contained a Ce6 coating which could be activated with a red laser. The authors tracked the growth of the tumors over 16 days and then, at the end of the experiment, placed tumors under a microscope to search for the particles. They reported that tumors treated with the new system contained 3.7 times as many particles, which penetrated 3.5 times deeper, compared with tumors treated with the previous device, which ultimately slowed their growth significantly compared to all other groups.
Review About Dual--Frequency Magnetic Particle Spectroscopy
March 06, 2025 Hans-Jochim Krause and Ulrich Engelmann wrote a new review published in Advanced Science (https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202416838). The fundamentals of frequency mixing magnetic detection (FMMD) as a special case of magnetic particle spectroscopy (MPS) are reviewed, elaborating its functional principle that enables a large dynamic range of detection of MNP. The latest applications of FMMD in nanomaterials characterization as well as diagnostic and therapeutic biomedicine are highlighted: analysis of the phase of the FMMD signal characterizes the magnetic relaxation of MNP, allowing to determine hydrodynamic size and binding state. Variation of excitation amplitudes or magnetic offset fields enables determining the size distribution of the particles’ magnetic cores. This permits multiplex detection of polydisperse MNP in magnetic immunoassays, realized successfully for various biomolecular targets such as viruses, bacteria, proteins, and toxins. A portable magnetic reader enables portable immunodetection at point-of-care. Future applications toward theranostics are summarized and elaborated.
Hans-Jochim Krause and Ulrich Engelmann wrote a new review published in Advanced Science (https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202416838). The fundamentals of frequency mixing magnetic detection (FMMD) as a special case of magnetic particle spectroscopy (MPS) are reviewed, elaborating its functional principle that enables a large dynamic range of detection of MNP. The latest applications of FMMD in nanomaterials characterization as well as diagnostic and therapeutic biomedicine are highlighted: analysis of the phase of the FMMD signal characterizes the magnetic relaxation of MNP, allowing to determine hydrodynamic size and binding state. Variation of excitation amplitudes or magnetic offset fields enables determining the size distribution of the particles’ magnetic cores. This permits multiplex detection of polydisperse MNP in magnetic immunoassays, realized successfully for various biomolecular targets such as viruses, bacteria, proteins, and toxins. A portable magnetic reader enables portable immunodetection at point-of-care. Future applications toward theranostics are summarized and elaborated.
European School of Magnetism 2025 (ESM2025) : Opening of Registration
January 20, 2025The next session of the European School on Magnetism (ESM) is scheduled from the 30th of June to the 11thof July 2025. It will be held in a mixed format. Attendees can either participate onsite, Liège, BE, or online. The number of onsite participants is limited to 100, online to 80. Requests for participation can be made from today until the 28th of February 2025.
The topic for ESM2025 is Topology for low Energy Spintronics. Bertrand Dupé, from the University of Liège and Flavio Abreu Araujo, from the University of Louvain, are chairs of the School.
Liège has excellent bus and train connections to major European. Depending on the requests for online participation, we may also organize local hubs in Europe, in which online participants may gather to attend the school together. The aim is to enhance the online experience through collaborative work, emulation and mentoring of local experts in the field of magnetism.
The School is addressed mainly at PhD students and post-docs, with either experimental or theoretical backgrounds. Similar to previous editions of ESM, the 2024 School aims at providing a thorough insight into magnetism through a broad series of fundamental lectures, and to address a specific topic of current interest in more detail. It consists of approximately 40 hours of lectures, practicals and tutorials, and round tables. During the school, the onsite students have free access to a library on magnetism. Attendees will be able to present their own work during poster sessions. The detailed program is available from the website:
http://magnetism.eu/school/2025/program
Magnetic Particle Meeting in 2025: Frontiers in Biomagnetic Nanoparticles in Telluride
January 13, 2025 If you are itching to go to a relevant magnetic particle meeting in-between our magnetic carrier meetings (which only take place in even years), you might consider our "sister conference" Frontiers in Biomagnetic Nanoparticles that will be held from June 30 - July 2, 2025 in beautiful Telluride, Colorado, USA. The meeting is organized by Thompson Mefford (Clemson University) and Jennifer Andrew (University of Florida). The program's 5 confirmed invited speakers are Randall Erb, Isaac Torres-Diaz, Emilie Secret, Hari Srikanth and Gabriela Romero Uribe. Check it out at
If you are itching to go to a relevant magnetic particle meeting in-between our magnetic carrier meetings (which only take place in even years), you might consider our "sister conference" Frontiers in Biomagnetic Nanoparticles that will be held from June 30 - July 2, 2025 in beautiful Telluride, Colorado, USA. The meeting is organized by Thompson Mefford (Clemson University) and Jennifer Andrew (University of Florida). The program's 5 confirmed invited speakers are Randall Erb, Isaac Torres-Diaz, Emilie Secret, Hari Srikanth and Gabriela Romero Uribe. Check it out at
https://www.magneticnanoparticle.com/.
You can get a hotel discount of $100 before January 15, and the deadline for abstracts is on February 12.
Hologic Completes Acquisition of Endomagnetics Ltd
October 07, 2024MARLBOROUGH, Mass.--(BUSINESS WIRE)-- Hologic, Inc. (Nasdaq: HOLX), a global leader in women’s health, has completed its previously announced acquisition of Endomagnetics Ltd (Endomag), a privately held UK-based developer of breast cancer surgery technologies, for approximately $310 million.

Endomagnetics breast cancer surgery technologies (Photo: Business Wire)
“We are thrilled to complete the acquisition of Endomag and are looking forward to working with our new colleagues to increase access to their innovative technologies, which complement and diversify our expanding interventional breast health portfolio,” said Erik Anderson, President of Breast and Skeletal Health Solutions at Hologic. “With our shared commitment to advancing women’s health globally, we are excited to improve outcomes for patients and, together with our customers, redefine the standard of care for breast cancer intervention.”
The transaction adds Endomag’s wireless breast surgery localization and lymphatic tracing solutions – including the Magseed® marker, the Magtrace® lymphatic tracer and the Sentimag® platform – to Hologic’s breast surgery portfolio, providing breast surgeons and radiologists with an expanded range of options and enhanced user experience.
“We are so proud of the company we built and the practice-changing breast surgery technologies that we developed following years of relentless research, innovation and deep engagement with clinicians,” said Eric Mayes, PhD, Chief Executive Officer of Endomag. “As we embark on this new journey with Hologic, I am filled with optimism about the opportunities for our team, our forthcoming innovations and our ability to impact even more women around the world.”
For more info: https://www.endomag.com/en/
SPICE Website: Magnetism Meets Plasmonics
August 15, 2024 You can now find at the SPICE website the links of the talks of the workshops “Spin textures: Magnetism meets Plasmonics”. We hope you enjoy the tutorials and talks from this exciting workshop.
You can now find at the SPICE website the links of the talks of the workshops “Spin textures: Magnetism meets Plasmonics”. We hope you enjoy the tutorials and talks from this exciting workshop.
We encourage you to visit the SPICE’s website (http://www.spice.uni-mainz.de/) for upcoming workshops that you may want to attend and to propose your own workshop. As always, all the talks of the workshops and on-line seminar are available at the SPICE YouTube channel, although for navigational purposes you may find it easier to find the video links on the SPICE website.
The Magnetic Carrier Meeting 2024 in Barcelona, Spain Was a Huge Success
July 01, 2024The 14th International Conference on the Scientific and Clinical Applications of Magnetic Carriers took place in Barcelona, Spain from June 17-21, 2024, with 252 participants from 33 countries. It was once again a great gathering of people with an interest in all things magnetic particle related. So many great talks, posters, discussions and interactions!
If you want to know more of what happened during those 5 days, check out this link.
For more information, check out our Archives.
September 2017
Search this site with the power of

